A Comprehensive Guide to the Lightning Network
Table of content
⚡️ What does Lightning Network do?
The Lightning Network is a game-changing second layer of the Bitcoin blockchain, allowing users to securely engage in transactions without needing them to be listed on the main chain. It consists of payment channels that connect participants and enable fast, cost-effective exchanges directly between each other. This off-chain solution not only offers faster transactions but also provides added protection that cannot compare with traditional networks.
⚡️ Is the Lightning network secure?
It's considerably more hazardous to acquire bitcoins through Lightning than it is to receive regular payments.
⚡️ Who uses the Lightning Network?
Users can send and receive “tips” about bitcoins through the (LN) on Twitter. Many of Twitter's 360 million monthly active users can send bitcoin payments to other Twitter accounts immediately and for free thanks to the Lightning Network-compatible payment app Strike.
⚡️ Does the Bitcoin Lightning Network have a coin?
It's paramount to understand that the (LN) does not create a new cryptocurrency, it simply uses Bitcoin’s infrastructure. Furthermore, its decentralized nature allows users access without permission levels and is implemented using open source code. The network also provides confidence in its safety as transactions are conducted on the well-known Bitcoin blockchain with smart contracts for secure off-network settlements.
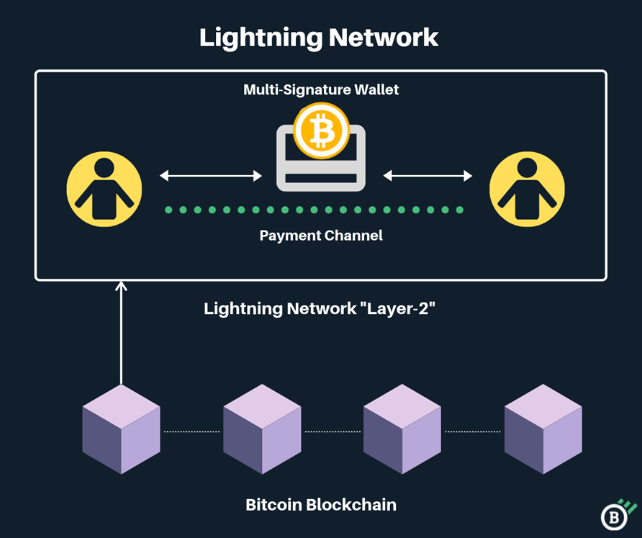
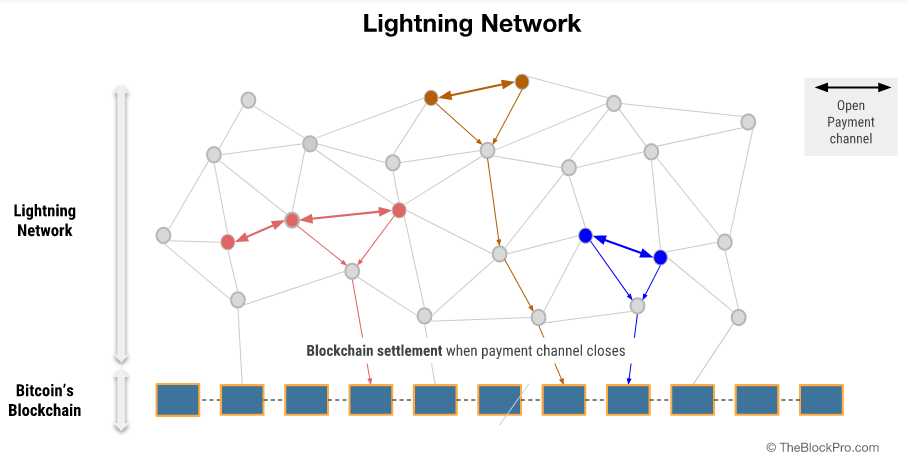
The Lightning Network is a second layer that consists of numerous payment channels between individuals or Bitcoin users. This network is built over the Bitcoin blockchain (BTC) and allows off-chain transactions.

The Lightning Network channel is a two-way transaction method in which people may send or receive payments from each other. The second layer improves the scalability of blockchain apps by organizing transactions not on the primary blockchain network (layer one), but still being able to utilize its power.
A cryptocurrency's wide-scale use is often limited by its scalability. A blockchain network can handle millions to billions of transactions per second when scaled properly, for example. When settlements and transaction fees are lowered off the network via (LN), it allows for new applications like instant micropayments. This could potentially answer the “can you buy coffee with Bitcoin?” problem that plagues many would-be users.
Despite its advantages, the Lightning Network has a few security pitfalls. Users must be aware of these risks to protect their coins from being lost when using the network.
Even though the Lightning Network is still in its nascent stages, it possesses a few potential risks yet to be seen. For instance, this technology may contain bugs or unexpected technical issues as it continues to evolve.
Despite any doubts, the (LN) could turn out to be a breakthrough for Bitcoin and cryptocurrency as a whole. This is an immensely significant step forward in blockchain technology that may one day realize Bitcoin's original potential of being used worldwide.

The Lightning Network's history is short but eventful
In 2015, Thaddeus Dria and Joseph Poon revolutionized the cryptocurrency world with their thought-provoking article “The Lightning Bitcoin Network,” which outlined the development of a groundbreaking new concept: The Lightning coin network. These ideas were discussed by Satoshi Nakamoto previously, and Mike Hearn shared these conversations with bitcoin developer Satoshi Nakamoto in 2013.
The article delves into the utilization of off-chain payment channels in its abstract. These external financial operations provide a method for two unknown parties to securely and rapidly transact money without putting extra strain on the network, regardless of how much data their transaction generates. Visa's peak performance was 47,000 transactions per second during one exceptionally busy period — demonstrating that such an approach can be extremely efficient and powerful.
Though Bitcoin blocks are currently limited to seven transactions at present, it would take a great deal of time for the network to match Visa's TPS if the average block size was restricted to one megabyte. In its early days, each transaction in Bitcoin measured approximately 300 bytes and only permitted up to 7 transactions per second – clearly disparate from today’s state-of-the-art blockchain technology.
Furthermore
In 2016, Driya and Poon founded Lightning Labs (now CoinDesk) to intensify research of the Lightning Network token. The personnel have changed ever since yet they remain dedicated to making the protocol work with Bitcoin's mainstream platform. By 2017, there was a SegWit-based soft fork which enabled more data per block; this led to a crucial advancement for the network's ability.
Investing in the Lightning Network is a decision already proven lucrative for many. When Lightning Labs first released their token, LNT, people could purchase it at $0.25 each during an initial coin offering in March 2018. Since then, its value has skyrocketed and as of June 2019 one token cost $0.70! Don't miss out on this golden opportunity; join those experiencing success through investing in the Lighting Network today!
How does Lightning work?
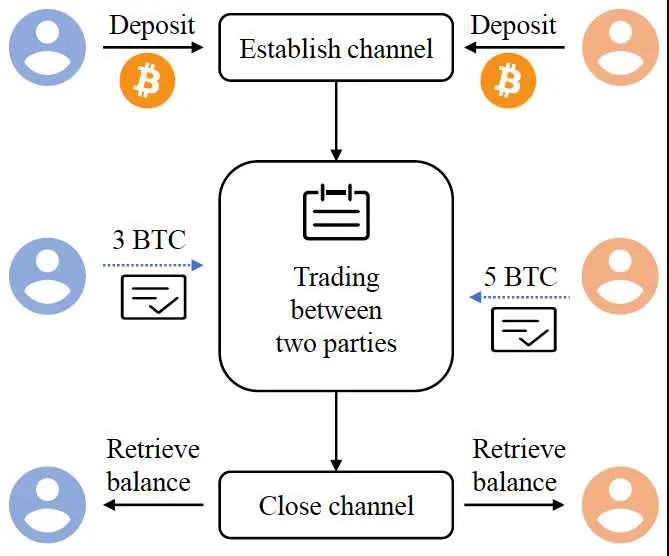
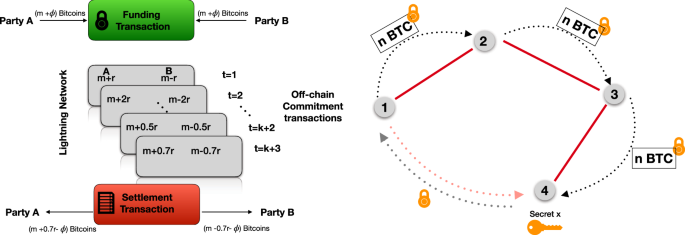
Through the Lightning Network, users are able to establish trustless channels between themselves and other parties, enabling secure transactions of cryptocurrency without having to involve a third-party. With this technology, trading digital assets is faster, easier and more efficient than ever!
When participants fund these channels, they can send an infinite number of transactions with no fees. Upon closure of the channel, the updated ledger is immortalized on a permanent blockchain and accessible to all users.

(LNT) token channels are “bidirectional,” meaning that both parties have to agree to the terms of the channel before it can be opened. This setup prevents one party from taking all of the funds in a channel without the other party's consent.
In order to open a channel, both parties must contribute cryptocurrency to a “funding transaction” which is then broadcasted onto the blockchain. The funding transaction is not finalized until both parties agree to it.

No longer do financial transactions require blockchain technology. With their system, both parties are able to trade goods and services upon commencement – all records of the transaction safely stored in a ledger accessible by each participant.
Pros of Lightning Network
The Lightning Network's major benefits are faster and cheaper transactions, allowing micropayments that have never been possible before. Users would have to pay expensive fees for a simple transaction and wait an hour or more for confirmation if the Lightning Network isn't used. Because miners prefer to verify bigger transactions because they get greater payment, the waiting time for smaller transactions would become even longer.

The Lightning Network is an extra security measure that runs on top of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Users may make transactions on the main blockchain for bigger purchases and Lightning Network off-chain for smaller ones without having to worry about security. Payment channels in the (LN) allow for private transactions, as long as no one sees each transaction individually but only the overall package.
The cryptocurrency world is on the cusp of a breakthrough: atomic swaps. This revolutionary technology enables users to swap one crypto for another without relying on an intermediary or a third-party exchange. Atomic swap technology is more advantageous than exchanges since it allows for almost instantaneous conversion with minimal costs or wallet transfers.

The Lightning Network has certain drawbacks
To maximize the potential of the Lightning Network, you'll require a wallet equipped to execute it. While it is not difficult to locate a wallet that works with the (LN), the user must first fund it from a conventional bitcoin wallet.
Those who wish to move their bitcoin from a regular wallet into the Lightning Network must first be prepared to pay a fee. Consequently, part of their bitcoin is lost in the process. Before being able to make payments through the Lightning Network, users have to first lock their bitcoins into a payment channel.

Sending bitcoins across wallets can be time-consuming and costly, which deters new users. Conversely, certain wallets can process both in-network and out-of-network payments without fees.
Before withdrawing, a party within the payment channel must close the channel and return their bitcoins to spend them.nnel and return them before spending them.

It is also challenging to terminate a cash flow and leave the channel open. Even closing or opening a payment channel necessitates that both parties make a preliminary transaction, known as a routing fee, which is impossible to do simultaneously. While opening the channel is simple in theory, all of those extra expenses add up to make it more expensive than many potential users are willing to pay.
Lightning Network's most significant issue is called Offline Transaction Fraud. If one person wants to close the payment channel while another person is offline, they could potentially steal their money. And if the victim reconnects to the network, it would be hard to track down and prosecute the thief since they may have already gone offline again.

Despite its advantages, the Lightning Network also has certain drawbacks that must be addressed. For example, outgoing payments that fail to pass validation are known as hanging payments. When it comes to verification, the Bitcoin Network will reimburse a stuck payment; however, due to the greater priority given to genuine transactions over stopped ones when compared with the past, it may take a while. The Lightning Network's design also means that a user must have an online node to process his or her payments, which is not the case with Bitcoin.

Ultimately, even if Lightning Network can address all of its obstacles, there remains the looming issue of government regulation. Regulators may find it difficult to understand Lightning Network enough to pass appropriate legislation. If regulators fail, major cryptocurrency users may also have trouble using (LN).
Even if lawmakers understand the tech, they may not allow Lightning Network because it is anonymous. Because legislators can only observe the concluding transaction after a user shuts their payment channel, instead of every single transaction, regulators might be skittish about approving it.
What Does the Lightning Network Look Like in the Future?
Luckily, the Lightning Network is seeing more and more use. According to DappRadar, there is over $110 million worth of bitcoins locked up in Lightning transactions. This could be anything from paying for products or services to using apps, gambling, and other activities.
Some applications are required for network usage, such as Lightning Network-compatible wallets. Because Lightning Network is a distinct protocol from the main Bitcoin network, users need a different sort of wallet to establish payment channels.

As the usage of the Lightning Network (LN) extends globally, a rapidly increasing number of users will desire to use wallets specifically designed for traders. We can help reduce transaction times on this network by dedicating ourselves as node operators. To meet user demands and accommodate these changes, we need more robust wallet solutions that are tailored to traders who want secure and reliable transactions with lightning speeds!
The Lightning Network is swiftly gaining traction among businesses and organizations. Despite still being in its formative stage, the technology has become noticeably more intuitive – making it straightforward to comprehend why enthusiasm for this innovation is rapidly increasing. As some features are examined during their beta period, you may experience occasional malfunctions or delays when using certain aspects – just like most other blockchain-based systems.

Traders can withdraw small amounts of bitcoin quickly and cost efficiently using exchanges that deploy the Lightning Network– even with a high volume of traffic on the network. Nonetheless, users may still be subject to inconvenient delays and costly transaction fees, as warned by Takeoff's Vitalik Buterin.
A marketplace for Lightning-based information has also been launched. When a payment channel is closed, the funds in it are locked—but some nodes may go down from time to time, leaving their payment channels open to fraudulent transactions. Instead of leaving the channel unguarded, a participant may pay a modest fee to the watchtower and provide a signal if a fraudulent transaction is detected.

What are Lightning Network nodes?
Even though the proposed Bitcoin Lightning Network will run off-chain, it will still require nodes to interact with each other to transfer funds and monitor the underlying Bitcoin blockchain.
Nodes on the Lightning Network are responsible for monitoring the blockchain to make sure no one is stealing any funds. Each node needs to keep track of who is transferring what money within each channel. Bitcoin nodes are dependable for verifying every transaction, yet only need to validate the reliability of those transactions they receive.
Three teams of developers are already working to create Lightning Network nodes—Lightning Labs, ACINQ, and Blockstream. When will the Bitcoin Lightning Network go into effect? The Bitcoin Lightning Network is still new, with only 14,339 nodes online as of November 2020. These nodes are spread out over 35,201 active channels. The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a noteworthy development for this digital currency, even though it may not be able to resolve all of Bitcoin's troubles.
Did you know that the Lightning Network can also be used to transact with other altcoinspeer-to-peer, such as Litecoin? Investing a few moments to understand this technology is invaluable.
This guide has introduced the Lightning Network: what it is, how it works, and its advantages and disadvantages. We hope you have found this information helpful in understanding the Lightning Network!