Ethereum crypto review and description of cryptocurrency
With Ethereum, you can send money to any other address just as quickly as with Bitcoin or any other cryptocurrency. Ethereum, like bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, lets you perform transactions digitally.
Table of content
- What is Ethereum?
- How Ethereum differs from the ether (ETH)
- What is the Ethereum Merge?
- How Ethereum works
- The DAO is a decentralized virtual organization. What Is Ethereum Classic and How Does It Work?
- Where does Ethereum originate?
- What is the process of Ethereum mining?
- What is gas in Ethereum
- What are the different Ethereum token types?
- What is Ethereum and how do I use it?
- What ETH is used for
- Is it possible to keep a transaction on the Ethereum network private?
- Is it possible to generate money using Ethereum?
- Scalability, ETH 2.0 and the future of Ethereum
- What is the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade?
- Ethereum and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Decentralized Ethereum Exchanges
- Nodes on the Ethereum Network and Mining
- Mining nodes for Ethereum
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a decentralized platform that runs smart contracts applications with zero possibility of fraud or third-party interference. Although Ethereum shares some characteristics with Bitcoin, it goes beyond being a digital currency. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the depths of Ethereum from its basics to advanced concepts.
- What it is.
- How to use it, where to buy it.
- If investing in Ethereum is worthwhile.
Moreover, Ethereum crypto has a much broader range of use than just currency; it can also be used to run any type of code and communicate with programs written by others. The Ethereum platform's greatest strength is its adaptability since its main objective is to create and manage code on a distributed network instead of one centralized server. In action, these applications are indelible and irrevocable.
How Ethereum differs from the ether (ETH)
Despite being widely misconceived, Ethereum's digital currency is not called ether. While the protocol bears its name, ETH is actually what it uses for accounting purposes and transactions.

What is the Ethereum Merge?
In September 2022, the Ethereum network will initiate its shift from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake which is known as the Ethereum Merge. This revolutionary transformation of consensus mechanism could revolutionize cryptocurrency once again and bring a new era to blockchain technology.
Ethereum ran on proof of work when it first started, the same system Bitcoin uses. The main con of this method is that a lot of energy is required, which has caused Bitcoin to use more power per year than in some countries.

Bitcoin provides users with a secure and innovative payment method, employing cryptography for extra security as the transactions are stored on the blockchain. Transactions are verified by network nodes and recorded in a public distributed ledger called the blockchain. The blockchain is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked and secured using cryptography.
Bitcoin is often regarded as a first-generation blockchain. Because of its simplicity, it is comparable to other rivals in the market. Bitcoin is a purposely strict protocol that prioritizes trustworthiness over usefulness. The capacity to execute intelligent contracts is severely restricted in Bitcoin and needs to be better suited for use-case situations beyond simple transaction execution.
Conversely, second-generation blockchains are not only more adaptable but also have superior operational capabilities. Rather than just providing support for standard financial transactions, they can sustain programmable transfers as well. For example, Ethereum cryptocurrency offers developers countless opportunities to build decentralized applications (DApps), allowing them to unleash their creativity and explore various coding possibilities.
Cryptocurrency is a rising industry, and ether currently sits as the second most valuable digital asset behind Bitcoin with its impressive market capitalization.

Ethereum is the de facto leader among second-generation blockchains, and its well-known status reflects this fact. It's comparable to bitcoin but can execute considerably larger transactions. This is where bitcoin and Ethereum's primary distinctions begin.
How Ethereum works
Ethereum crypto is an immutable “state machine” – you can essentially observe the balances of all users and smart contracts at any given moment. Once something sets off a state shift, every node needs to update its records to reflect the new status.
Smart contracts are activated by transactions, either from other contracts or end-users. Each node of the network runs the contract code and records its outcome as soon as a user sends it an order. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) translates instructions into a language that computers can quickly and effortlessly comprehend.
Mining is the process responsible for updating Ethereum's state of play. This crypto asset follows a similar Proof-of-Work algorithm to Bitcoin, allowing users to mine it with ease.

The DAO is a decentralized virtual organization. What Is Ethereum Classic and How Does It Work?
Ethereum provides opportunities for novel interactions on the internet; one example is a decentralized autonomous organization or DAO. A DAO is controlled by code and functions like a computer program, which demonstrates how Ethereum allows for unique ways of interacting online. The DAO was one of the first and most ambitious attempts to establish such a community. The organization was governed by complex smart contracts and intended to be an autonomous venture capital fund. The tokens of the DAO were distributed during an ICO, to allow investors to have voting rights in the organization.
Following the launch, hackers utilized a bug in The DAO contract to steal about a third of all funds. It had trapped 14% of the total ether issuance at the time. The event had the most severe consequences for the new initiative. In reflection, the developers decided to do a hard fork of the chain, resulting in its division into two. In one network, the transactions of the attackers were “reversed” to return the money to its rightful owners. This version of the blockchain is now known as Ethereum. The original chain's transaction history was preserved – it is now known as “Ethereum Classic.”
The disastrous results of these events were a stark reminder of the risks and consequences related to entrusting massive amounts of money to autonomous code. Decisive action was required, which is what caused such an uproar within the blockchain community. Subsequently, Ethereum underwent a hard fork that gave rise to two distinct cryptocurrencies: ETH, and ETC. It marked one of the most significant moments in crypto history as it showed how strong popular opinion could be when making decisions together on this platform.
Where does Ethereum originate?
How do new ether tokens get made?
Ether is mined, an important part of maintaining and updating the network's data. Miners receive new ether when blocks are added to the Ethereum network, just like bitcoin miners do.

What is the process of Ethereum mining?
The security of the network is dependent on mining. Blockchain verification is made simpler with the elimination of a central administrator, ensuring that updates are done in an accurate and secure manner. Miners utilize their computing power to solve cryptographic puzzles during mining. This is how blocks are “hashed out.” To be acknowledged as genuine, a block's hash must match the unknown value specified by the protocol. As the network grows, with more miners joining and attempting to solve a hash puzzle, its difficulty level correspondingly rises. Thus, it takes a greater amount of time for one to conquer this challenge.

Because of this, other miners determine the difficulty of the Ethereum crypto network more than ever before. Because so many people are looking for answers at once, hash transactions generally tend to be as quick as possible, known as a hash rate. As the network's total hash rate expands, it becomes increasingly difficult to solve mining problems. Once a valid answer is determined and broadcasted on the internet, all nodes confirm its accuracy; if most of them deem it legit, the block gets added to the blockchain accordingly and miners get rewarded with ether.
What is gas in Ethereum
Let's look at the previous example of a smart contract from Part 1 again. It was a straightforward agreement that didn't require much computing power to execute. Nevertheless, a savvy contract does not function solely on your own computer; instead, you interact with all of the nodes in Ethereum's cryptographic network to ensure its execution.

What happens if hundreds of thousands of nodes in the network run a sophisticated contract? What if someone sets up their contract to execute the same code over and over, clogging up the network's nodes? To address this issue, Ethereum employs the term “gas.” Although a car cannot drive without fuel, contracts cannot function without gas. Gas is an integral part of any contract to operate; it serves as a measure, indicating the amount of work needed for each transaction or function on Ethereum's network.
This is the Ethereum network's fee-collecting mechanism in a nutshell. It also applies to regular transactions – miners will refuse to approve the movement of money from one wallet to another if the user's price is too low.
It's worth noting that gas and ether are not the same things. Gas prices vary greatly, depending on the miners. You pay a commission to execute an operation in ETH when you conduct a transaction. Ethereum is comparable to bitcoin in this respect since both have inflationary currencies that are limited in quantity but have no set value.
Each transaction consumes a specific quantity of gas required for its completion, but the cost of gas may differ. Complex transactions require far more gas than simple ones. To precisely gauge the processing capacity needed for a particular job, gas is used as a unit of measurement. Thanks to this system, it's much simpler to monitor and figure out a reasonable fee depending on how much energy is consumed.
What are the different Ethereum token types?
Ethereum is fascinating because it allows the creation of custom assets on the blockchain that may be stored and transmitted similarly to ether. Developers possess total command over the regulations that regulate a token's behavior, enabling them to mold it as they deem fit. They can establish how many tickets will be created, their creation process and also transferability rules.
Tokens allow developers much creativity and innovation with new use cases for technology and economic models. For various applications, tokens can serve as their currency, be backed by tangible assets, and perform multiple other functions. New methods for utilizing Ethereum tokens are being developed regularly, offering possibilities that did not exist previously.
What is Ethereum and how do I use it?
If you'd like to purchase GAME on Binance, it couldn't be simpler! With the peer-to-peer market, you can purchase ETH conveniently with many payment methods. Alternatively, using this page as a resource to buy ETH could work for you too – the choice is yours!

What ETH is used for
Ethereum, unlike bitcoin, is not only designed to function as a money network. The platform enables a variety of decentralized applications in which ethereum serves as programmable money. It's been used in decentralized finance and trading, exchanges, games, and other things like that.
Is it possible to keep a transaction on the Ethereum network private?
No. All transactions on the Ethereum blockchain are public. Although it's not necessary to provide your real name, experts can still correctly identify a considerable amount of users with precision using the publicly available data.
Is it possible to generate money using Ethereum?
Ether is a highly volatile asset, which means it may make and lose money at any time. Some people keep Ethereum for the long run hoping that the network will one day become a worldwide programmable payment system. Other traders seek to build up their holdings by trading ether for altcoins. In both cases, financial dangers exist.
The Ethereum blockchain, the centerpiece of the decentralized finance environment, also enables you to profit from lending, issuing synthetic assets using ETH as collateral, and stacking.

As an alternative to diversifying their portfolios, many investors elect to take a long-term approach and invest exclusively in bitcoin. Others, on the other hand, only invest in ether and hedge some of their funds against short-term rate changes. There is no one-size-fits-all approach that can be applied by all traders in the market.
Scalability, ETH 2.0 and the future of Ethereum
What is the correct definition of “scalability”?
Put simply, scalability is the potential of a system to grow. Servers and networks can be adapted in countless ways to meet growing demand. When it comes to cryptocurrency, scalability pertains to the capacity of a network to develop so that larger amounts of requests may be processed without compromising security or speed. It's noteworthy that blockchain networks are still in their infancy when it comes to development.

As the usage and renown of a network expand, so does its requirement to manage an increasing amount of transactions. Ethereum must be able to efficiently process an abundance of transactions if it hopes to satisfy the expectations of its users.
What is the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade?
Despite its enormous potential, Ethereum presently has significant limits, as shown by the scalability problem. To ensure Ethereum serves as the foundation of a more efficient financial system, it needs much greater capacity. The decentralized nature of this network makes this feat particularly difficult since no individual or entity can enforce its dictate on everyone else involved in the network.

To ensure the network is sufficiently decentralized, certain restrictions must be imposed. The harder it is to operate a node, the fewer people will take part in the system; this leads to centralization of authority. If transaction speeds are increased too much, then it can put at risk the integrity of that same network.
Another criticism that Ethereum has received is the high energy consumption of its existing Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism. Mining is used to add new blocks to the network, which has a negative association with high energy expenditures.

In order to solve several current issues, developers are introducing Ethereum 2.0 (or ETH 2.0 for short). This series of improvements have the potential to drastically improve the network's capabilities upon completion.
Ethereum and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Have you ever heard of Decentralized Finance?
Defi is the name given to a movement to decentralize the financial industry. Defi apps are built on public, open blockchains, allowing anybody to use them without permission from authorities or organizations, which sets them apart from conventional finance controlled by rules and institutions. Defi is essential in getting people interested in the new financial system.

Users in DeFi interact with smart contracts and one other through peer-to-peer networks. Whenever you use our service, your assets will remain firmly in your control. You never have to relinquish them to anyone else – ever. The Ethereum network is the most popular for DeFi apps since it is highly decentralized and has a large developer community.
What can DeFi accomplish?
The absence of a centralized manager to manage the network is one of bitcoin's most appealing features. Extend that notion to the financial industry and you have DeFi. The absence of middlemen or central networks means there is no single source that could lead to system failure.
Another benefit of DeFi is unrestricted access. Billions of people worldwide are denied access to basic financial services that would otherwise allow them to lead more prosperous lives. They are one of the key consumer categories in DeFi, according to the proposal.
Decentralized Ethereum Exchanges
DEXs, or decentralized exchanges, are platforms offering individuals the capacity to transfer assets securely from one wallet to another. ethereum trading on a regular exchange necessitates the placement of assets in an exchange account first, however this is not necessary with a DEX.
Decentralized exchanges, in particular, are an exception. They're protected against centralised wallet assaults but may be vulnerable to smart contract attacks. Uniswap, Kyber Network, and IDEX are examples of Ethereum blockchain-based decentralized exchanges.
Nodes on the Ethereum Network and Mining
What is an Ethereum node
Instead of being run on a single client, Ethereum employs a network of clients to execute smart contracts. Unlike bitcoin, which has only one official client implementation, Ethereum has many different ones. Bitcoin Core is the main software in bitcoin and performs this function in that currency. Geth is the most popular Ethereum client.
What are the functions of an Ethereum node?
Unlike bitcoin, which only has one official client implementation – Bitcoin Core – Ethereum is fueled by a network of different clients to execute smart contracts. Of these many options, Geth remains the most commonly used Ethereum client today.
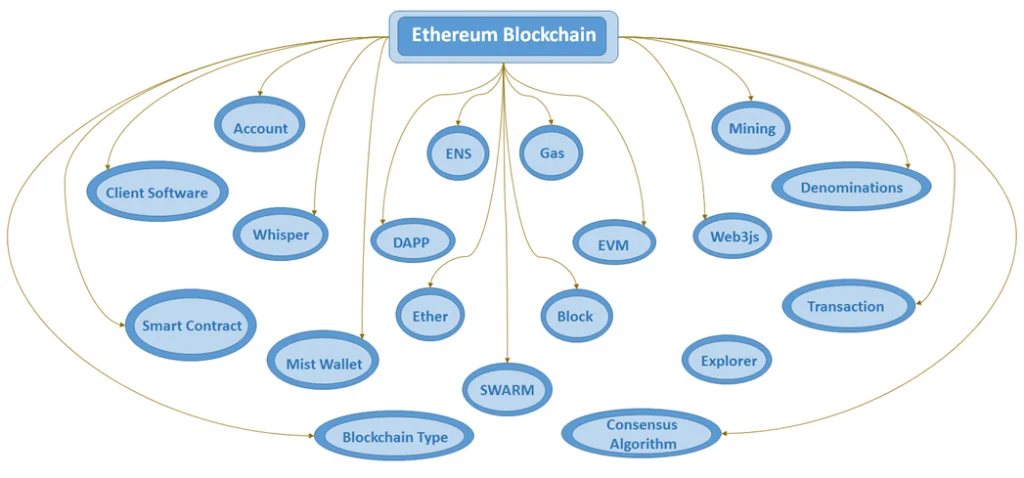
Mining nodes for Ethereum
A mining node can run either a full or restricted client. Mining farms, which are specialized setups of equipment, are generally utilized for Ethereum mining. To speed up the hashing process, they typically contain many video cards.
Ethereum miners have two options: solo mining, in which they develop the currency alone, or pool mining. Solo mining means you'll work on your own to discover blocks. Miners pool their resources and divide the rewards equitably when they mine as part of a pool. This helps to lower the risks associated with mining.
Ethereum mining was once a profitable short-term investment, however with its upcoming switch to Proof of Stake miners will be looking for new options. It is time to look away from Ethereum and towards additional networks that offer long-term rewards and the chance to mine other cryptocurrencies too!
Mining Ethereum is not a straightforward process; it requires you to obtain graphics cards or ASICs, access cheap power sources, and set up both a mining operation and an Ethereum wallet. This demands ample time investment as well as financial commitment for successful results.
⚡️ Which is better than Bitcoin or Etherium?
The amount of electricity used by bitcoin is 707 kW, whereas that of ether is 62.56 kW. The complex algorithms in the bitcoin blockchain are carried out using advanced processors. Ether's low power consumption makes it a more environmentally friendly cryptocurrency.
⚡️ How long does it take to mine 1 Etherium?
About 7.5 days
⚡️ How to start mining ETH?
✔️ Step 1 – Install GPUs and set up your computer.
✔️ Step 2 – Get an Ethereum wallet (Mist or MyEtherWallet)
✔️ Step 3 – Join an Ethereum mining pool.
✔️ Step 4 – Start mining!
⚡️ Is ETH 2.0 a new coin?
This isn't a new currency, and won’t alter the ETH you possess. When it comes to Ethereum and Ethereum 2.0, Eth2 is simply a patch that will improve the Ethereum blockchain. Because of the two final phases, the complete release is anticipated until at least 2023.
⚡️ How many transactions per second will Ethereum 2.0 have?
100,000 transactions per second