What Are Crypto Exchanges and How Do They Work
This article is a simple guide to cryptocurrency exchanges, where you can trade digital currencies like Bitcoin. We explain how to use these platforms, including how to start trading their security features and what the top exchange platforms are. We also discuss how these exchanges make money and briefly describe the different types: Centralized, Decentralized, and Hybrid exchanges.
Table of content
Key Takeaways
- What Are Crypto Exchanges: They are online platforms where you can buy or sell digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Features: These exchanges offer different trading options, ensure quick trades, and have strong security to protect your money.
- Using an Exchange: To start trading, you need to sign up, deposit money, and then you can buy or sell cryptocurrencies.
- Making Money: Exchanges earn money mainly by charging fees for each trade you make.
- Types of Exchanges: There are three kinds: Centralized Exchanges (easy to use and suitable for large trades), decentralized exchanges (more secure and private, but can be harder to use), and hybrid exchanges (mixed features of both centralized and decentralized exchanges).
How Do Crypto Exchanges Work?
These exchanges serve as the middleman between buyers and sellers. They are essential for the liquidity and accessibility of various cryptocurrencies.
Key Features of Crypto Exchanges
Crypto exchanges come with a variety of features, including:
- Trading Pairs: Exchanges offer a variety of trading pairs, such as BTC/USD or ETH/BTC, letting users trade one cryptocurrency for another or for fiat currency.
- Order Types: Users can place different orders, market, limit, and stop orders, to execute trades according to their strategies.
- Liquidity: High liquidity means enough buyers and sellers on the platform to fill orders quickly and at current prices.
- Security Measures: Reputable exchanges implement robust security measures like two-factor authentication (2FA), cold storage for funds, and encryption to protect users' assets and data.
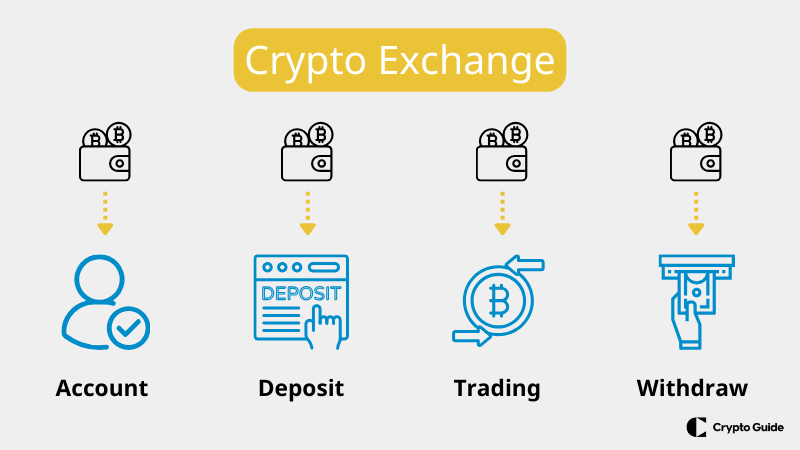
How to Use a Crypto Exchange
People use online platforms to buy digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, treating them as investments for the future. Because the prices of cryptocurrencies change a lot, some people also trade them frequently to make quick profits by buying when prices are low and selling when they're high.
Besides investing and trading, some people also use cryptocurrencies to pay for things where they are accepted, making them more common in daily life. Some crypto exchanges give users a physical payment card which can be used to pay for goods and services. It is a popular way to use trading and investing profit.
For this, you need a crypto exchange, and to use such a platform, follow these general steps:
1. Create an Account: Verify your identity as required by the exchange's Know Your Customer regulations.
2. Deposit Funds: Deposit cryptocurrency or fiat money into your exchange account using the provided methods.
3. Trading: Navigate the trading interface to buy or sell cryptocurrencies. You can analyze price charts and use various tools to make informed decisions.
4. Withdraw Funds: you can withdraw funds to your wallet or bank account after trading.
How Do Exchanges Make Money?
Understanding crypto exchanges and how they operate is crucial for anyone looking to engage in the digital currency market. Now, let's explore the various revenue streams that enable these exchanges to make money.
Trading Fees
One of the primary ways that crypto exchanges make money is through trading fees. These are small percentages taken from each trade executed on their platform. Here's how it works:
- Maker-Taker Fees: Exchanges often use a maker-taker fee model, where the maker (the person providing liquidity to the market by placing a limit order) pays a lower fee than the taker (the person taking liquidity away by filling orders).
- Volume-based Discounts: To motivate high-volume trading, many exchanges offer lower fees for users who trade large amounts of cryptocurrency.
- Withdrawal and Deposit Fees: In addition to trading fees, exchanges may charge fees for depositing and withdrawing funds. Those are fixed fees – flat fees for withdrawals and deposits, regardless of the amount. Also, percentage-based fees – a percentage of the transaction amount – can be more cost-effective for smaller transactions.
- Listing Fees: New cryptocurrencies often seek to get listed on popular exchanges to increase their visibility and credibility. Exchanges can charge one-time listing fees (flat fees to review and potentially list a new cryptocurrency) or ongoing costs (additional fees for maintaining the listing and providing support).
- Spread: The spread is the difference between a cryptocurrency's buy and sell price. Exchanges can profit from this spread by buying low and selling high. They can set the buy price slightly lower and the sell price slightly higher than the market average, profiting from the difference.
- Custodial Services and Wallet Fees: Some exchanges offer custodial services, holding cryptocurrencies on behalf of users. They may charge for storage Fees (for providing secure storage of digital assets) or insurance (optional insurance coverage for assets held in custody).
- Other Revenue Streams: Exchanges may have additional revenue streams, such as:
– Staking: Allows users to earn rewards by locking up specific cryptocurrencies, with the exchange taking a cut of the staking rewards.
– Crypto lending: Crypto lending on exchanges allows users to lend their cryptocurrencies to others in exchange for interest, while the exchanges make money by charging fees for these transactions.
– Market Data and API Access: Selling market data or access to their trading API to institutional or algorithmic traders.
Exchanges and Their Fees
To illustrate, here are some real-world examples:
- Binance: Known for its relatively low trading fees, which can be further reduced using its native BNB token.
- Coinbase: Charges a percentage-based fee for transactions and has a more user-friendly interface, which may attract beginners willing to pay a premium for ease of use.
FAQ About Crypto Exchanges
What do crypto exchanges do?
A crypto exchange is a platform where users can buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies. Users create accounts, deposit funds (fiat currency like USD or cryptocurrencies), and place orders to buy or sell.
What are the 3 main types of crypto exchanges?
A single entity owns Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) and enables crypto trading. Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) are peer-to-peer, facilitating direct user transactions without intermediaries. Hybrid Exchanges combine CEX efficiency with DEX security and privacy.
Are crypto exchanges safe?
Crypto exchanges vary in safety; some implement strong security measures, while others may be more vulnerable to hacks. It's important to research and use reputable exchanges with a good track record and to enable additional security features like two-factor authentication.
What is the safest crypto exchange?
It's difficult to say which crypto exchange is the safest, as security can be subjective and depends on various factors. However, Kraken is widely considered one of the safer options in the industry, known for its robust security measures and good reputation.
Can you exchange crypto for real money?
Yes, you can exchange cryptocurrency for real money through online exchanges, peer-to-peer transactions, or cryptocurrency ATMs.
Types of Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Understanding the different types of cryptocurrency exchanges is crucial for investors and traders looking to engage with the crypto market.
Centralized Crypto Exchanges (CEX)
Centralized exchanges are the most prevalent type of crypto exchanges, operating as intermediaries between buyers and sellers. They are managed by a centralized organization that controls the exchange's operations. Examples of Centralized Exchanges include Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
Advantages
- User-Friendly Interface: Many CEXs offer intuitive platforms that are easy for beginners to navigate.
- High Liquidity: Centralized exchanges typically have higher trading volumes, ensuring liquidity and enabling users to execute large trades with minimal impact on the market price.
- Advanced Features: They often provide additional services like margin trading, futures, and options.
- Customer Support: CEXs usually have dedicated support teams to assist users with queries or issues.
Disadvantages
- Security Risks: Being centralized, they are more susceptible to hacking and security breaches.
- Regulatory Oversight: CEXs are subject to government regulations, affecting their operations, and may lead to personal data collection.
- Withdrawal Limits: There may be restrictions on the cryptocurrency you can withdraw within a specific timeframe.
Decentralized Crypto Exchanges (DEX)
Decentralized exchanges operate without a central authority, facilitating direct peer-to-peer transactions on a blockchain. Examples of Decentralized Exchanges include Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap.
Advantages
- Security: With no central point of failure, DEXs are less vulnerable to hacking.
- Privacy: Users retain control of their private keys and personal information.
- Censorship Resistance: Transactions are complex to censor or interfere with due to the decentralized nature of blockchain.
Disadvantages
- Lower Liquidity: DEXs often have lower trading volumes than CEXs, leading to higher price slippage.
- Complexity: They can be less user-friendly, especially for those new to the cryptocurrency space.
- Limited Features: DEXs typically do not provide advanced trading options like margin trading.
Hybrid Crypto Exchanges
Hybrid exchanges combine the best features of both CEXs and DEXs, offering a balance between security, privacy, and functionality.
Advantages
- Enhanced Security: Hybrid exchanges can provide a DEX's security benefits while offering the customer support and user experience of a CEX.
- Regulatory Compliance: They may offer a degree of regulatory compliance while providing privacy features.
- Versatility: Users can enjoy advanced trading features in a more secure environment.
Disadvantages
- Complexity in Operation: Fusing centralized and decentralized elements can make the platform more complex to manage and use.
- Emerging Technology: As a relatively new concept, there may be fewer examples in the market, and the technology may not be as tested as that of more established exchanges.
Top 10 Cryptocurrency Exchanges Ranked by Volume (2026)
The volume of trades on an exchange is one of the key indicators of its liquidity and overall health. In 2026, the landscape of top exchanges by volume continues to evolve, reflecting the dynamic nature of the market.
Below is a list of the 10 top cryptocurrency exchanges ranked by volume in 2026. Please note that the trading volume can fluctuate daily, and the rankings might change accordingly.

1. Binance
- Key Features: Offers various coins, futures, and margin trading with competitive fees.
- Volume Indicator: Consistently holds the top spot for trading volume, indicating high liquidity and user trust.
2. Coinbase
- Key Features: Known for its user-friendly interface and regulatory compliance, making it a favorite among U.S. traders.
- Volume Indicator: Maintains a strong position in the market with a significant volume of USD trading pairs.
3. Bybit
- Key Features: Offers a user-friendly trading platform with a fast engine, great customer service, and support in many languages for all levels of crypto traders.
- Volume Indicator: Bybit offers trading in 536 cryptocurrencies, 6 traditional currencies, and has 775 market pairs. The most traded pair on Bybit is ETH/USDC.
4. Kraken
- Key Features: Renowned for robust security measures and a wide selection of fiat-to-crypto pairs.
- Volume Indicator: Holds a steady volume with a loyal user base, especially in Europe.
5. Bitfinex
- Key Features: Provides advanced trading features and charting tools for professional traders.
- Volume Indicator: High volume, particularly in the BTC/USD and ETH/USD trading pairs.
6. HTX Global
- Key Features: Offers a comprehensive list of cryptocurrencies and a dedicated token, HT, which can be used for trading fee discounts.
- Volume Indicator: Sustains a high volume, particularly in the Asian market.
7. Bithumb
- Key Features: It is one of the largest South Korean exchanges known for its Korean Won (KRW) trading pairs.
- Volume Indicator: Significant volume, largely driven by the local South Korean market.
8. OKEx
- Key Features: Provides various services, including spot and derivatives trading.
- Volume Indicator: Features a high volume with a strong presence in Asian markets.
9. Bitstamp
- Key Features: One of the oldest exchanges, it is known for its reliability and easy-to-use interface.
- Volume Indicator: Consistent volume focusing on major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
10. KuCoin
- Key Features: Offers various altcoins and user-friendly trading services.
- Volume Indicator: Known for its competitive trading fees and promotions that boost its volume.
Final Words on What is Crypto Exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges are vital platforms for engaging with digital currencies, offering various services from buying and selling to complex trading. They combine user-friendly features with robust security measures to ensure safe and efficient transactions.
Whether you choose a centralized, decentralized, or hybrid exchange, each type offers unique advantages tailored to different trading needs. Understanding these platforms is essential for anyone looking to buy or trade cryptocurrencies.







