Staking Crypto: What is & How it Works
Table of content
What is Staking?
Crypto staking is a way of earning rewards by holding onto specific cryptocurrencies. It is a process by which you lock up your coins for a certain period to help secure the blockchain network. In this article, we explore crypto staking in detail.
How Does Staking Work?
Staking is a fundamental concept in many blockchain networks, particularly those using the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism or one of its variants. It's a process that allows network participants to lock up a certain amount of the network's native cryptocurrency in a wallet to participate in the blockchain's operations, including validating transactions, securing the network, and creating new blocks.
Here's a simplified explanation of how staking works:
Understanding Proof of Stake
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Unlike Proof of Work (PoW), which requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new blocks, PoS relies on participants, known as validators or speakers, who lock up some of their cryptocurrencies as a stake in the network.
- Selection for Validation: The PoS algorithm selects validators to create a new block based on the size of their stake and other factors, which can include the length of time they've held the stake, randomness, and other network-specific criteria.
The Staking Process
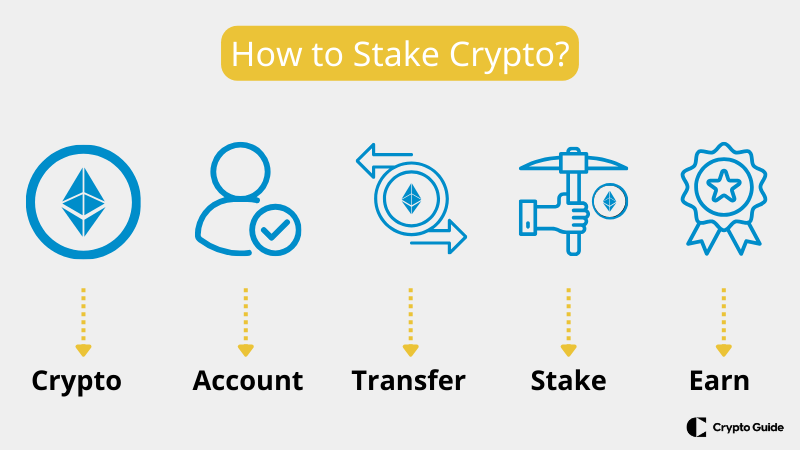
- Choose a cryptocurrency that supports staking. Many different cryptocurrencies support staking, so you must choose the one you want. Some popular staking cryptocurrencies include Ethereum, Cardano, Tezos, and Cosmos.
- Create an account with a staking platform. There are many different staking platforms available, so you will need to choose one that you trust. Some popular staking platforms include Coinbase, Kraken, and Binance.
- Transfer your cryptocurrency to your staking platform account. Once you have created an account with a staking platform, you must transfer your cryptocurrency to your account. This will allow you to stake your coins.
- Start staking your cryptocurrency. Once your cryptocurrency is in your platform account, you can start staking it. This will involve locking up your coins for a certain period. The exact time will vary depending on the cryptocurrency and the staking platform.
- Earn rewards. In exchange for staking your coins, you will earn rewards, typically in the form of additional coins or tokens. The exact rewards will vary depending on the cryptocurrency and the staking platform.
Staking is a great way to earn passive income on your cryptocurrency holdings. It is also a way to help support the blockchain network that you are invested in. However, doing your research before you start staking your coins is essential. Risks are involved, such as losing your coins if the staking platform goes bankrupt or is hacked.
Ways of Staking Cryptocurrency
In the digital finance world, there are many ways to stake cryptocurrency to earn rewards. Staking involves locking up some of your digital coins to help a blockchain network run smoothly. In return, you get extra coins as rewards. Here, we’ll explore each method of staking, showing how they work and what they offer to those who participate.
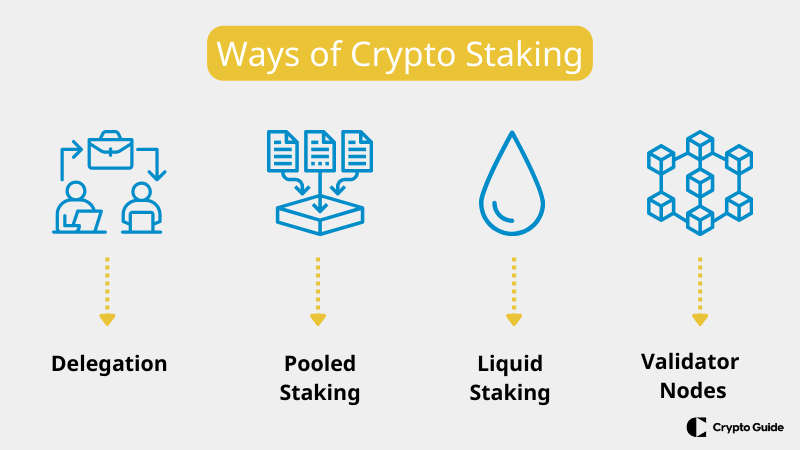
Delegation (Delegated Staking)
In delegated staking, cryptocurrency holders delegate their tokens to a validator (a node that participates in the consensus mechanism). This allows token holders to earn staking rewards without having to run a node themselves. It's a popular option for those looking to participate in staking with minimal technical involvement.
Benefits of Delegation:
- Ease of Use: Simplified staking process without needing to manage nodes or maintain software.
- Accessibility: Available to those without technical expertise or time commitment for direct staking.
- Risk Diversification: Spreads risk across multiple validators, potentially reducing exposure to individual node issues.
How Delegation Works?
- Choose a Validator: Select a reputable validator with a good reputation and a history of reliable performance.
- Delegate Your Coins: Transfer your staked coins to the chosen validator, who includes them in their overall stake.
- Earn Proportional Rewards: Receive staking rewards based on the amount of coins delegated and the validator's performance.
Factors to Consider:
- Validator Reputation: Choose a validator with a proven uptime, reliability, and security track record.
- Commission Rates: Compare commission rates across different validators to find one that best aligns with your preferences.
- Network Participation: Check the validator's activity and contribution to the consensus mechanism.
- Platform or Exchange Support: Ensure the platform or exchange you use supports delegation to the chosen validator.
Pooled Staking
Pooled staking involves combining resources with other token holders to increase the chances of being selected to validate transactions and earn rewards. It's ideal for those who may not have enough tokens to meet the minimum staking requirements or wish to mitigate risk by diversifying.
Benefits of Pooled Staking:
- Accessibility and Simplicity: Provides a straightforward staking process for individuals without technical expertise or time commitment.
- Reduced Minimum Staking Requirements: Allows participation with smaller amounts of staked coins, lowering the entry barrier.
- Increased Chances of Rewards: The likelihood of earning rewards is enhanced by pooling resources with a larger group.
- Risk Diversification: Spreads risk across multiple participants, minimizing the impact of individual node issues.
How Pooled Staking Works?
- Join a Staking Pool: Choose a reputable staking pool that adheres to best practices and security standards.
- Transfer Staked Coins: Migrate your chosen cryptocurrency from an exchange or external wallet to the staking pool.
- Share in Rewards: Receive proportional staking rewards based on your contribution to the pool's stake.
Factors to Consider:
- Pool Reputation: Select a pool with a proven uptime, reliability, and security track record.
- Commission Rates: Compare commission rates across different pools to find one that aligns with your preferences.
- Pool Performance: Evaluate the pool's historical performance in earning rewards and maintaining uptime.
- Fee Structure: Understand the fees charged by the pool, such as withdrawal or management fees.
Liquid Staking
This method allows participants to stake their tokens and receive a liquid token in return, representing their staked investment. These liquid tokens can be used within the DeFi ecosystem, providing liquidity while still earning staking rewards. It addresses the liquidity issue inherent in traditional staking.
Benefits of Liquid Staking:
- Enhanced Liquidity: Users can access the value of their staked assets without unstaking, facilitating DeFi participation.
- Reduced Risk of Impermanent Loss: LSTs can hedge against temporary price fluctuations in the underlying asset, reducing impermanent loss risk.
- Diversification Potential: Users can allocate their LSTs across different DeFi protocols and strategies.
- Accessibility for Smaller Stake: Liquid staking allows participation with smaller amounts of staked assets, lowering the entry barrier.
How Liquid Staking Works?
- Token Lock-up: Users lock up their staked tokens with a liquid staking provider.
- Receipt Token Issuance: The provider issues liquid tokens (LSTs) representing the user's staked assets and staking rewards.
- Liquidity Utilization: Users can use their LSTs in DeFi activities while the provider stakes the underlying assets.
- Staking Rewards: Users earn staking rewards on their locked-up tokens, which are reflected in the LSTs.
Factors to Consider:
- Provider Reputation: Choose a reputable liquid staking provider with a proven security and transparency track record.
- Token Utilization: Understand LSTs' liquidity options and associated risks.
- Fee Structure: Familiarize yourself with the fees charged by the liquid staking provider, such as withdrawal or management fees.
Validator Nodes
Running a validator node involves participating directly in the blockchain's consensus mechanism. Validators confirm transactions and create new blocks. This option requires significant technical knowledge, hardware, and often a substantial minimum stake. It's suited for highly involved participants who are committed to the network's security and performance.
A validator node is crucial to proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain networks. It is a computer responsible for verifying and processing transactions, maintaining the network's consensus mechanism, and earning rewards for participating.
Key Responsibilities of Validator Nodes:
- Block Validation: Validator nodes review and confirm the authenticity of transactions before adding them to the blockchain.
- Consensus Participation: Validator nodes participate in the consensus mechanism, which ensures the network's security and integrity.
- Reward Earning: Validator nodes earn rewards for contributing to the network's security and transaction validation.
How Validator Nodes Work?
- Staking: Validator nodes stake their cryptocurrency holdings as a security deposit to demonstrate their commitment to the network.
- Block Creation: Validator nodes compete to create new blocks by proposing valid transaction bundles.
- Consensus Mechanism Participation: Validator nodes reach a consensus with other nodes to approve new blocks and maintain the blockchain's integrity.
- Reward Distribution: Validator nodes receive rewards for their participation, which is proportional to their stake and contribution to consensus.
Role of Validator Nodes in PoS Networks:
- Security: Validator nodes play a vital role in securing the network by verifying transactions and maintaining the consensus mechanism.
- Decentralization: Validator nodes contribute to the network's decentralization by distributing the responsibility of consensus among multiple participants.
- Network Throughput: Validator nodes help maintain the network's throughput by verifying and processing transactions efficiently.
- Economic Incentive: Validator nodes are motivated to participate by the prospect of earning rewards, which incentivizes them to maintain the network's health.
FAQ About Staking Crypto
How much on average I can earn by staking crypto?
The average annual return for staking crypto is between 5% and 15%.
Is staking crypto safe?
Staking crypto is generally considered to be safe, but there are some risks, such as liquidity and validator risks.
Is staking better than holding?
Staking crypto can be a more profitable way to invest than holding, but it also comes with more risk.
How does crypto staking work?
Staking can earn passive income by locking up your cryptocurrency to support the blockchain network.
How long does staking crypto last?
Staking crypto involves risks such as liquidity constraints—your funds are locked and inaccessible for a period—and market volatility, which can reduce the value of your staked assets.
How are Staking Rewards Calculated?
The calculation of staking rewards depends on the specific blockchain network and its consensus mechanism.
Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
Staking rewards are typically expressed as an annual percentage yield (APY). APY is the total percentage of rewards that you can expect to earn on your staked cryptocurrency over a year. It considers both the base interest rate and any compounding that occurs.
Base Interest Rate
The base interest rate is how you earn rewards on your staked cryptocurrency. This rate is determined by the blockchain network and its consensus mechanism. For example, the base interest rate for Ethereum 2.0 is currently around 4.6%.
Compounding
Compounding is when your rewards are added to your staked cryptocurrency, and you start earning rewards on your rewards. This can significantly increase your APY over time. For example, if you have an APY of 10% and compound your rewards daily, you will earn about 31% more over a year than if you did not.
Lockup Period
Many blockchain networks require you to lock up your cryptocurrency for a certain period before you can unstake it. This is to prevent people from taking advantage of the system by staking and unstaking their cryptocurrency frequently. The lockup period can vary depending on the blockchain network and your chosen staking provider.
Total Rewards
Your total rewards will depend on the cryptocurrency you stake, the base interest rate, the compounding frequency, and the lockup period. You can use a staking calculator to estimate how much you will earn in rewards.

Here is an example of how staking rewards are calculated:
Assumptions:
Staking reward rate: 5% per year (APY)
The initial amount of staked ETH: 1 ETH
Calculation:
- 30 days:
- Staking rewards = (1 ETH * 0.05 * 30) / 365
- Staking rewards = 0.0041096 ETH
- 60 days:
- Staking rewards = (1 ETH * 0.05 * 60) / 365
- Staking rewards = 0.00821917808 ETH
- 90 days:
- Staking rewards = (1 ETH * 0.05 * 90) / 365
- Staking rewards = 0.01232876712 ETH
- 120 days:
- Staking rewards = (1 ETH * 0.05 * 120) / 365
- Staking rewards = 0.01643835616 ETH
As you can see, the longer you stake your ETH, the more rewards you will earn. This is because the staking reward rate is compounded over time. With careful planning and consideration, staking can be a great way to earn passive income on your cryptocurrency holdings and support the blockchain networks you care about.
*It is important to note that these are just estimates, and the actual amount of staking rewards you earn will vary depending on the specific staking pool you are using and the overall market conditions.
TOP 5 Staking Coins
Let's dive into the “Top 5 Staking Coins,” highlighting the best cryptocurrencies for staking. These coins are chosen for their good rewards, stability, and how they improve the blockchain world. Here, we'll look at why these coins are worth considering for anyone interested in staking.

Ethereum
Ethereum (ETH) is the most popular cryptocurrency in the world and has one of the most active staking communities. Staking ETH allows you to earn rewards while helping to secure the network.
Binance
Binance (BNB) is the native token of Binance Exchange, the largest cryptocurrency exchange in the world. Staking BNB allows you to earn rewards while helping to secure the Binance Chain network.
Polkadot
Polkadot (DOT) is a multi-chain network that connects different blockchains. Staking DOT allows you to earn rewards while helping to secure the network and participate in governance decisions.
Solana
Solana (SOL) is a high-performance blockchain that aims to rival Ethereum regarding scalability and speed. Staking SOL allows you to earn rewards while helping to secure the network.
Cardano
Cardano (ADA) is a cryptocurrency designed to be more scalable and efficient than Ethereum. Staking ADA allows you to earn rewards while helping to secure the network.
Why Can't You Stake All Cryptocurrencies?
Not all cryptocurrencies can be staked because staking only works for specific blockchains that use a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. In a PoS network, validators, who are participants who stake their cryptocurrency holdings, are responsible for validating transactions and ensuring network security. They are randomly selected to validate transaction blocks and rewarded with additional cryptocurrency for their participation.
For staking to be possible, the blockchain network needs to have specific characteristics, including:
- Decentralization: PoS requires a decentralized network with many participants to ensure its security and efficiency.
- Tokenomics: The cryptocurrency must have a sufficient supply and market capitalization to support staking and network stability.
- Technical Infrastructure: The blockchain network must have the infrastructure to handle the staking process, including mechanisms for selecting validators, validating transactions, and distributing rewards.
- Community Support: The cryptocurrency project should have a strong community that supports staking and contributes to the network's governance.
If these conditions are not met, staking may not be feasible or sustainable for the blockchain network. Additionally, some cryptocurrencies may choose not to implement staking, opting for other consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) or delegated Proof-of-Stake (dPoS).
Benefits of Staking Crypto
Passive income: Staking offers a way to earn passive income, rewarding participants with additional tokens for supporting the network.
Network security: Stakers enhance blockchain security and integrity, helping prevent attacks and ensuring smooth operation.
Energy efficiency: Compared to Proof of Work (PoW) mining, Proof of Stake (PoS) and staking are more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Governance rights: Some networks offer stakers governance rights, allowing them to vote on important decisions affecting the future of the protocol, such as upgrades and policy changes. This empowers users with a stake in the network's success to influence its direction.
Reduced volatility: Staking can potentially reduce the volatility of a cryptocurrency. When tokens are locked up for staking, it reduces the circulating supply, which can lead to more stable prices, especially for tokens with significant staking participation.
Community engagement: Being involved in staking often encourages deeper engagement with the project's community. Stakers tend to be more invested in the project's success and may participate more actively in discussions, development proposals, and community events.
Increased network participation: Staking mechanisms encourage broader participation in the blockchain network, democratizing access to the validation process. This can lead to a more robust and decentralized network.
Risks of Staking Crypto
Liquidity: When you stake your cryptocurrency, it is locked up or committed to the consensus mechanism. This means you cannot access or trade your staked funds for some time. The specific unbinding period will vary depending on the cryptocurrency and the staking platform. During this time, you cannot sell your coins to take advantage of market fluctuations, which could negatively impact your returns.
Market volatility: The value of your staked coins may also fluctuate, potentially impacting your overall returns. If the price of the cryptocurrency drops, the value of your staked rewards will also decrease. This is similar to any other investment that you make in the cryptocurrency market.
Validator risks: If you delegate your stake to a validator, you trust them to secure the network and distribute your rewards correctly. You could lose your staked coins if the validator is malicious or incompetent. It is essential to do your research and choose a reputable validator.
Protocol changes: The staking protocol of a cryptocurrency could change in the future, affecting your ability to stake your coins or the rewards you earn. It is important to stay current on the latest developments and adapt your staking strategy accordingly.
Regulatory risks: The cryptocurrency space is a rapidly evolving and increasingly regulated industry. New regulations that affect the profitability or legality of staking could be introduced.
Taxes: Staking rewards may be taxable in some jurisdictions. It is important to consult with a tax advisor to understand your tax obligations.
Despite these risks, staking can be a profitable and rewarding way to invest in cryptocurrency. However, it is important to understand the risks involved and to make informed decisions before committing your funds.
Conclusion
Staking is locking up cryptocurrency assets to engage in a blockchain network's consensus mechanism, earning rewards like additional coins. It offers passive income, contributes to network security, and can be a profitable investment with associated risks.
Staking is exclusive to cryptocurrencies with a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, requiring careful research due to its complexity. Before participating, it's crucial to evaluate specific staking processes, weighing risks and rewards to make informed decisions that support the desired blockchain networks while earning passive income on cryptocurrency holdings.




![Top 10 Best Crypto Staking Platforms for [year]](https://betoncrypto.io/app/uploads/2024/12/cryptostaking.webp)

![Best Cryptos to Stake in [year]](https://betoncrypto.io/app/uploads/2024/11/image1-4.webp)
