Staking Risks in Crypto
Staking crypto is a way to earn passive income by locking up your cryptocurrency and helping to secure the network. However, there are risks involved with staking crypto, which we will explore in this article.
Table of content
Risks of Staking Crypto
There are some crypto staking risks, but they are generally less than the risks associated with other types of cryptocurrency investments, such as trading. The most common risks are explained below.
Market Risk
Market risk is the risk that the value of your staked cryptocurrency will go down. This is because the cryptocurrency market is volatile, and prices can fluctuate wildly. If the price of your staked cryptocurrency goes down, you will lose money on your investment.
To eliminate market risk, you should only stake cryptocurrency that you are comfortable holding for the long term. You should also diversify your portfolio by staking a variety of different cryptocurrencies.
Lockup Duration
The lockup duration refers to the period during which you cannot access or trade your staked cryptocurrency. This is a common practice among Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains as it involves a long-term commitment to the network and helps maintain network stability.
This period varies depending on the specific cryptocurrency and staking platform. Some platforms may have a lockup period of only a few days, while others may have a lockup period of several months or even years.
A significant disadvantage of this lockup period is for crypto traders who want to have access to their funds at all times. If you need to sell your staked cryptocurrency before the lockup period is over, you may have to pay a penalty.
Loss or Theft of Assets
Loss or theft of assets is a major concern for crypto traders. Cryptocurrencies can be stolen through a variety of methods, including hacking, phishing scams, and social engineering.
There are a few things that you can do to protect your cryptocurrency from loss or theft. First, choose a reputable cryptocurrency exchange or wallet. Second, make sure that your cryptocurrency is stored in a secure location. Third, be careful about what websites and links you click on and what information you share online.
Even if you take all the necessary precautions, there is still a risk that your cryptocurrency could be lost or stolen. This is why it is important to only invest money that you can afford to lose.
Reward Duration
Reward duration refers to the length of time it takes to receive staking rewards. The reward duration for staking can vary depending on the cryptocurrency and the platform. Some platforms distribute rewards daily, while others distribute rewards weekly or monthly.
There are a few reasons why reward duration is important. First, it can help to create a steady stream of income for stakers. If rewards are distributed frequently, stakers can more easily plan their finances and make informed investment decisions.
Second, reward duration can help to attract more stakers to the platform. If rewards are distributed frequently, stakers are more likely to stake their cryptocurrency on the platform. This can help to increase the security of the network and make it more profitable for stakers.
Validator Risks
Validator risks refer to the risks that stakers face when they delegate their cryptocurrency to a validator. Validators are responsible for validating transactions and adding blocks to the blockchain. If a validator misbehaves, they may be slashed, meaning they will lose a portion of their staked cryptocurrency.
Validator Costs
Validator costs are an additional cost that stakers may have to pay when staking their cryptocurrency. Typically, the validator receives payment for the services they provide, such as validating transactions and adding blocks to the blockchain. The amount of validator costs can vary depending on the cryptocurrency and the platform.
There are a few reasons why validator costs are important:
- First, they can help to cover the costs of running a validator node. Validator nodes require hardware and software infrastructure, as well as electricity and bandwidth. Validator costs can help to ensure that validators have the resources they need to keep the network running smoothly.
- Second, validator costs can help validators to act responsibly. By charging stakers for their services, validators have a financial incentive to keep the network secure and efficient. This is because if a validator misbehaves, they may lose their stakers, which would mean that they would no longer receive validator fees.
What is Crypto Staking?
Staking is the process of locking up your cryptocurrency in a wallet or platform to participate in the network's security and earn rewards. This is done by delegating your staked cryptocurrency to a validator, who is responsible for confirming transactions and ensuring the integrity of the network.
Staking is a new idea in the cryptocurrency world, but it's gaining popularity among investors who want to earn passive income on their holdings.
The rewards for staking can vary depending on the cryptocurrency and the platform, but they typically range from 2% to 10% per year.
How Does Crypto Staking Work?
The staking process is similar to earning interest on a bank account, but instead of earning money from a financial institution, you earn cryptocurrency from the blockchain network.
Staking is possible because of the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. It's a consensus mechanism used in blockchain networks, where participants (often referred to as validators or stakeholders) are chosen to create and validate new blocks and secure the network based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
PoS is a more energy-efficient alternative to the proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism used by most cryptocurrencies. Under PoS, validators are randomly selected to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain. The more cryptocurrency you stake, the more likely you are to be selected as a validator.
When you stake your cryptocurrency, you are essentially lending it to the validators, participants in a blockchain network responsible for verifying and validating transactions to secure the network and maintain its integrity. In return, they will pay you a reward for helping to secure the network. The staking rewards can vary depending on the cryptocurrency and the platform.
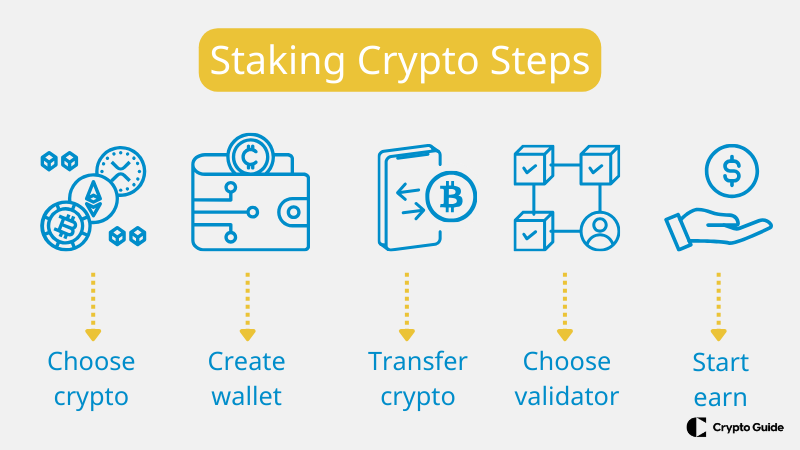
Here are the steps involved in staking crypto:
- Choose a cryptocurrency that supports staking. A growing number of cryptocurrencies support staking, including Cardano, Tezos, Cosmos, and Solana.
- Create a cryptocurrency wallet. You will need a cryptocurrency wallet to store your staked cryptocurrency. Many different wallets are available, including software wallets, hardware wallets, and exchange wallets.
- Transfer your cryptocurrency to your wallet. Once you have created a wallet, you will need to transfer your cryptocurrency to it. This can be done through an exchange or directly from another wallet.
- Choose a validator. Once your cryptocurrency is in your wallet, you will need to choose a validator to delegate your staked cryptocurrency to. Validators are responsible for validating transactions and adding blocks to the blockchain. You can choose a validator based on their reputation, experience, and fees.
- Start earning rewards. Once you have delegated your staked cryptocurrency to a validator, you will start earning rewards. The rewards will be paid to your wallet regularly, such as every week or month.
Staking is a relatively simple process, but it is important to do your research and understand the risks involved before you start staking.
Conclusion on Staking Risks
While understanding the risks is vital, it’s equally important to first grasp what is crypto staking. Market fluctuations can significantly affect the value of staked assets, and the lockup period may restrict access to your funds. Staking through exchanges exposes investors to potential vulnerabilities, such as hacking. Technical issues within the staking process can also lead to financial losses, and maintaining a validator node involves extra costs.
Navigating these risks effectively requires a deep understanding of the crypto staking process.




![Top 10 Best Crypto Staking Platforms for [year]](https://betoncrypto.io/app/uploads/2024/12/cryptostaking.webp)

![Best Cryptos to Stake in [year]](https://betoncrypto.io/app/uploads/2024/11/image1-4.webp)
