What is bitcoins inflation?
Table of content
- After all, what exactly are crypto and inflation?
- Bitcoin crypto and inflation
- The argument against bitcoin being a deflationary asset
- Is inflation a positive or negative factor for the economy?
- Why is crypto and inflation significant to cryptocurrencies?
- The Advantages of a Firm Bitcoin Guarantee
- During a recession, what will happen to bitcoins?
- How can Bitcoin assist customers in the long run?
- After all, 21 million bitcoins have been mined; what will happen to the cryptocurrency?
- What happens to the value of bitcoin during a recession?
- In conclusion
⚡️Could Bitcoin be the ideal method of safeguard against inflation?
Bitcoin has the power to bring about a revolution in digital payments, with its unparalleled capacity to enable rapid and effortless transactions across boundaries. One of the most crucial advantages should not be overlooked when considering bitcoin.
⚡️ Will the expanding supply of bitcoins bolster the cryptocurrency market?
The recent decline in the cryptocurrency market clearly shows that it is not sufficient to protect against inflation of 7%. Modern technology has drastically transformed the financial landscape, from banking to buying and selling to payments. By leveraging this revolutionary development, we now have a plethora of resources at our disposal to enable us to make sounder financial choices. Unfortunately, cryptocurrencies are inadequate when it comes to battling rising inflation rates.
⚡️ Is Ethereum inflationary?
Ethereum, which was previously a purely inflationary currency, introduced EIP-1559 in August 2021, which burns tokens instead of passing them on to miners. During peak network usage, the burning rate caused the coin to deflate, implying that more coins were destroyed than created.
⚡️Can investing in bitcoin help protect your portfolio from the volatility of the stock market?
Bitcoin is designed to preserve its worth against inflation and thus guarantee long-term value. This is possible because only a finite number of Bitcoin, 21 million, can exist at any moment. With demand increasing over time, this scarcity will ensure Bitcoin's enduring value for years to come.
It’s been claimed that some investors have rushed into bitcoin to protect their assets from the damaging inflationary policies of governments. But exactly what does it imply?
As bitcoins inflation climbs, people are drawn to anything that might protect them from rising prices.
Cryptocurrency is often considered deflationary, and its supporters frequently market it as an asset class unrelated to tangible assets. However, understanding the complexities of cryptocurrencies and their varying inflationary rates can be a daunting task.
After all, what exactly are crypto and inflation?
Bitcoins inflation works exactly like any other currency: as time passes and its value decreases, the same amount of money can now buy fewer items. You'll know it's present when you watch shows from the '80s that show a burger being sold for 50 cents while in today's world, the cost is ten dollars! Inflation occurs quickly yet silently – but with Bitcoins, you have control over how much your digital wallet deflates.

When prices rise faster than your pay, you may have recognized the severity of inflation. You’ll be worse off if you cut your spending by 10% on $50,000 a year rather than last year’s $60,000 salary. However, if your employer raises your income to $55,000 per year, you won’t have to alter your lifestyle.
bitcoins inflation isn’t just about the prices of goods and services. It’s also about your salary and how much money you can save. The purchasing power of savings also diminishes during inflationary periods. So, people often seek to invest in assets that will hold their value or increase it at a rate greater than inflation.

Inflation is good for consumers, according to economists. However, in the face of an economic downturn, as with a coronavirus epidemic, excessive inflation can become a problem.
Economists have different theories for the present spike in bitcoins inflation, which is among the highest rates seen in decades. to combat a pandemic-inflicted recession, the government has been pumping money into the economy.
Some experts claim that the Federal Reserve isn't wholly responsible. The primary issue has been a scarcity of supply owing to blockchain.

Bitcoin crypto and inflation
Cryptocurrency opponents fear that allowing central banks to impact the economy through quantitative easings, such as by lowering interest rates, will create problems. Uncontrolled printing of money by central banks in Venezuela, Turkey, and Zimbabwe has devastated their economies.
Proponents of crypto often claim that cryptocurrencies, like bitcoin (BTC), are immune to central banks’ and governments’ bungling because they are decentralized and can’t be turned off.

Another reason is that bitcoin creation is programmed in code, unlike the Federal Reserve, which cannot just print as many bitcoins as it wants.
The rate at which fresh bitcoins are produced is regulated by the bitcoin protocol, ensuring that those who utilize this digital currency remain secure in their transactions. The supply is limited, and it is predicted that the supply of new coins will run out around 2140. Unlike central banks, whose economists must react to market changes, the Bitcoin blockchain operates in a consistent fashion.
Every four years, the protocol reduces the quantity of new bitcoins brought into circulation by half, a process known as “halving.

Some fans have compared Bitcoin’s fixed quantity to “digital gold,” comparing it to the yellow metal, another popular inflation-resistant asset. So-called asset value vaults survive the test of time since they are uncorrelated with other assets and resistant to third-party market manipulation. On the other hand, do cryptocurrencies like bitcoin truly guard against bitcoins inflation?
The argument against bitcoin being a deflationary asset
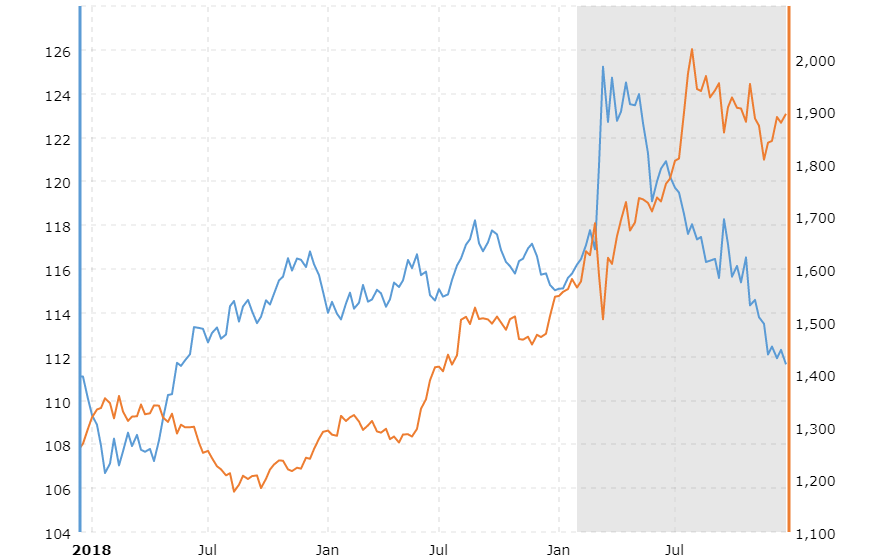
In the meantime, while the US dollar has tumbled, bitcoin far outpaced it, rewarding early investors. However, cryptocurrency is highly volatile: recent buyers who lost money when bitcoin plummeted can attest to this.

Over the previous several years, bitcoin has mirrored the performance of the United States stock market, which outperforms when the economy is expanding and stumbles when spending slows down-as it did in 1997. When inflation hit a 40-year peak in December 2021, bitcoin fell by more than 20 percent. It’s difficult to answer whether bitcoin is a long-term investment or a speculative bubble.
Nonetheless, only some cryptocurrencies work in the same manner as Bitcoin. As demand remains equal, some cryptocurrencies are deflationary; this means that the number of tokens accessible steadily decreases over time to raise their worth.
The US dollar-backed stablecoin TerraUSD has a dynamic stock; it creates and destroys tokens based on LUNA token exchanges to maintain the value fixed at $1.

Non-interchangeable tokens ( NFT ), for example, are one-of-a-kind – they’re like a work of art in that their worth is based on their scarcity.
Is inflation a positive or negative factor for the economy?
Inflation shrinks the purchasing power of money. Is this to say that inflation is bad? Not necessarily. Most economists believe that a little bit of inflation may benefit the economy. How does it work?

Inflation, on the whole, promotes consumer spending. It’s crucial to a country’s development, and the US Federal Reserve is trying to achieve an inflation rate of 2% in order to keep prices stable.
In a healthy economy, modest and steady rates of inflation are to be anticipated. Consumers and firms spend more money on items and services, which results in economic development. When demand outpaces supply, manufacturers increase their prices to meet the increased demand, causing bitcoins inflation. In this case, inflation may be considered as beneficial.
However, a significant price increase or decline too quickly is usually not an indication of good news. Price hikes induce customers to anticipate further rises in the future, resulting in greater demand. Producers are thus compelled to raise prices as a result of this trend. The term “hyperinflation” or “runaway inflation” refers to this pattern. It’s essential to remember that inflation is a normal economic development-but it can also get out of control.

The price deflation of a Deflationary Depression is marked by a long-term trend in which prices continuously fall. Consumers delay purchasing in anticipation of lower costs in the future as this occurs. Manufacturers also keep lowering prices to attract buyers, as demand drops.
Moderate bitcoins inflation benefits the economy in several ways, as it stimulates spending and promotes economic development.
Why is crypto and inflation significant to cryptocurrencies?
With the possibility of hyperinflation in traditional money, investors are drawn to invest even more heavily in digital currencies to protect against future currency devaluation. Cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin and ether ( ETH ) are a fantastic option for diversifying portfolios for investors looking for an alternative.

The Advantages of a Firm Bitcoin Guarantee
Scarcity is one of the keys to making an asset resistant to inflation. Because bitcoin has a restricted quantity, it continuously loses value, which is why it’s called “digital gold.
Satoshi Nakamoto, the inventor of Bitcoin, desired that the value of each Bitcoin unit should increase over time. This was secured by a fixed maximum supply and the low rate at which new Bitcoins are mined.

It is not feasible to produce a new bitcoin once the maximum number has been reached. Transactions will continue to be carried out as usual, and miners distributing the currency will still receive payment for their services in processing fees.
During a recession, what will happen to bitcoins?
Bitcoin was created from the Great Recession, also known as the “Great Financial Crisis.” Satoshi Nakamoto established Bitcoin to provide individuals with a currency that didn’t require a third party or central authority. A decentralized cryptocurrency emerged as a result.

As economic uncertainties persist in the current recession, bitcoins are soaring to unprecedented heights. Even during the COVID-19 pandemic, when other forms of investments have tanked, bitcoin has continued to increase its value significantly.
It is impossible to predict what will happen to bitcoins during a recession; nevertheless, recent years have revealed their tremendous resilience. Let us take heart then that if history offers any hints, bitcoin may just make it through another economic downturn unscathed.

During a recession, adverse economic effects can spread to countries with economic ties. Because Bitcoin is also inherently diversified, it can serve as a recession-proof asset. Unlike the U.S. dollar, which is influenced by GDP and other factors of the American economy, such as export prices, monetary policy, and currency demand, bitcoin remains unaffected by any nation's economic losses or gains.
How can Bitcoin assist customers in the long run?
Bitcoin is unlikely to topple major centralized currencies, but it has altered the financial system since its creation in 2009. Its technology has aided revolutionary improvements in decentralized finance (DeFi) and is beneficial to unbanked consumers throughout the world.

Blockchain technology has led to a slew of new developments, but its primary purpose is to serve people accurately. Blockchain technology’s fundamental feature is that it provides users with a safe, permission-free, and decentralized method to conduct financial transactions. Bitcoin and other crypto-assets provide a solid alternative to traditional currencies, protecting against inflation while allowing users to transact without government supervision.
Suppose you are in search of a lucrative long-term investment. Evidently, it's time to consider Bitcoin as the currency that could revolutionize our world's financial system and create a much-needed transformation.Taking advantage of this opportunity now may reward investors with tremendous returns at some point down the line.
After all, 21 million bitcoins have been mined; what will happen to the cryptocurrency?
The algorithm has decided that no further Bitcoin will be produced, yet miners remain motivated to mine blocks due to the attractive transaction fees they can earn.

What happens to the value of bitcoin during a recession?
At the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, Bitcoin prices fell moderately along with the stock market. However, by October investors started to take cryptocurrency seriously and pushed prices to an all-time high.
Some analysts are concerned that if the U.S. economy falls into recession next year, bitcoin's recent strong correlation to American stocks could mean bad news for cryptocurrency. These experts believe that how successful weather the storm is will depend largely on how other markets fare.
In conclusion
Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, are a way to protect against inflation. But recent studies have revealed something more – that Bitcoin shares remarkable similarities with other major asset classes like stocks! Consequently, investing in this option could be one of the shrewdest decisions you make for your portfolio.

When economic stability is jeopardized, central banks typically react by increasing interest rates or taking other measures to curb inflation. As a result, many assets often experience devaluation. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin have seen a surge in popularity recently. That said, some digital currencies have properties that should help them keep their value better than others over time. These include things like being rare (a limited supply), easy to move or trade without fees, and not subject to direct government control.
Diversifying your investment portfolio is key, and cryptocurrencies can provide that by spreading out the investments you have. Nevertheless, avoid placing too many resources in a single asset class.