What Is Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and How Does It Work?
Finance is changing because of decentralized finance, or DeFi. Instead of relying on traditional banks, DeFi uses blockchain technology to create a new financial system that's open to everyone.
But what is DeFi, how does it work, and could it be the future of finance? In this article, you will learn more about DeFi and its potential to change how we handle money.
Table of content
- Key Highlights
- What Is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
- How Does DeFi Work?
- Comparing DeFi vs CeFi (Centralized Finance)
- Decentralized Finance Components
- Insurance in DeFi
- Interoperability and Cross-Chain Protocols
- Regulatory Environment and Compliance
- Security Practices for Decentralized Finance Users
- Benefits of Decentralized Finance
- Risks and Downsides
- Real-World Examples
- The Future of DeFi
- FAQ About Decentralized Finance
Key Highlights
- Decentralized finance is a blockchain-based financial system providing lending and trading without banks.
- It uses smart contracts on decentralized networks for secure, automated transactions.
- DeFi includes exchanges, lending platforms, and yield farming to manage assets directly.
- It provides open access and user control, unlike traditional bank-managed systems.
- There are risks like hacks and contract vulnerabilities, making security a top priority.
- DeFi is accessible, transparent, gives users control, and can yield higher returns.
- The system is complex, risky, and largely unregulated.
- The potential for growth and integration with traditional finance exists, but better security and regulation are needed.
What Is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
DeFi is a fast-growing financial tool and service system based on blockchain technology. Unlike traditional finance, it doesn't rely on banks.
Instead, it's open to everyone and uses smart contracts to automate transactions and agreements. DeFi offers various financial services, such as lending, borrowing, staking, and insurance.
It is decentralized, transparent, and easy to use, potentially making finance more accessible globally.
How Does DeFi Work?
Decentralized Infrastructure
DeFi operates on decentralized networks, mainly using blockchain platforms like Ethereum and Solana. These networks are made up of nodes spread worldwide, each keeping a copy of the blockchain for transparency and security.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts written directly into code. In decentralized finance, they automate financial tasks like lending, borrowing, and trading. These contracts run on the blockchain and perform actions automatically when certain conditions are met.
User Interaction
People interact with DeFi protocols through decentralized apps (DApps), which are user-friendly interfaces. Users connect their crypto wallets, like MetaMask, to DApps for secure access to decentralized finance protocols.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Users use decentralized exchanges (DEXs) such as Uniswap or SushiSwap for cryptocurrency trading. There are other types of crypto exchanges that work differently, but DEX platforms allow direct trading between users without a central authority, with trades executed through smart contracts for transparency and security.
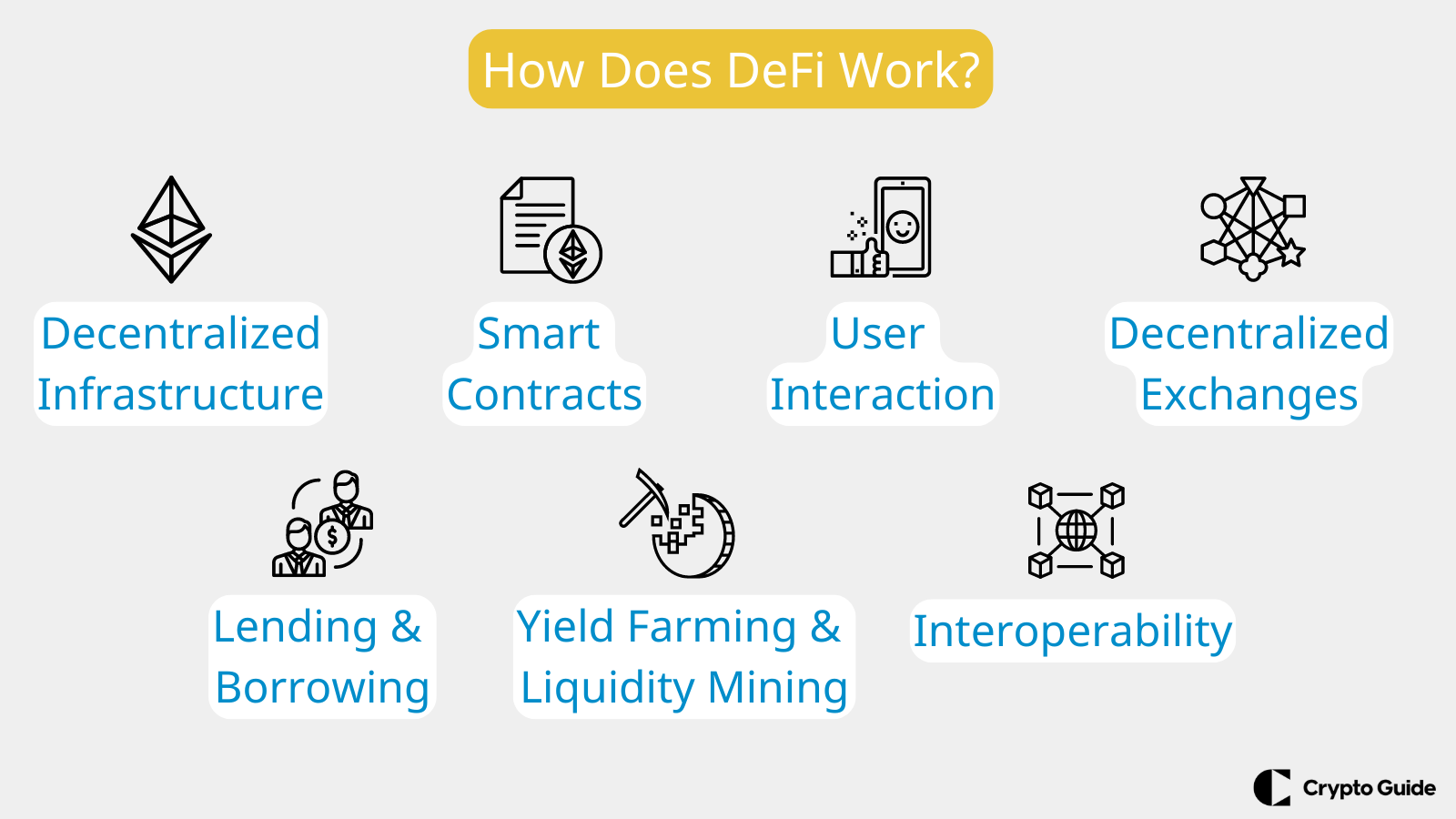
Lending and Borrowing
DeFi platforms offer lending and borrowing services through smart contracts. Users can lend their cryptocurrencies to earn interest or borrow assets by using their existing holdings as collateral. Platforms like Compound and Aave allow these transactions, with interest rates set algorithmically.
Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
Yield farming involves users providing liquidity to DeFi protocols in exchange for rewards, often in the form of additional tokens. Liquidity providers deposit their assets into liquidity pools, which are used for trades on DEXs. Additionally, they can explore other earning opportunities, such as liquid staking, where they receive rewards in tokens generated by the protocol.
Interoperability
DeFi protocols are designed to work together, allowing users to seamlessly access various financial services across different platforms. This interoperability combines different DeFi protocols to create more complex financial products and services.
Comparing DeFi vs CeFi (Centralized Finance)
DeFi and CeFi represent their own set of characteristics, advantages, and limitations:
Infrastructure
- DeFi runs on decentralized blockchain networks like Ethereum, with no central authorities. It uses smart contracts to handle transactions and agreements automatically.
- CeFi relies on centralized institutions such as banks and financial intermediaries to manage transactions and offer financial services.
Access
- Anyone with an internet connection and a crypto wallet can join DeFi without restrictions, as it offers open and permissionless access.
- Access to CeFi often requires identity verification and adherence to regulatory rules, limiting participation based on demographics or location.
Control
- With DeFi, users have full control over their assets and transactions, as they interact directly with smart contracts without intermediaries.
- Centralized entities control user funds and transactions, leading to potential risks such as censorship, freezing of accounts, and unauthorized access.
Transparency
- Transactions on DeFi platforms are visible and traceable on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Centralized platforms may lack transparency as they operate proprietary systems and databases, making it hard for users to verify transactions independently.
Security
- DeFi relies on cryptographic security and blockchain consensus mechanisms, which theoretically make it more resistant to certain types of attacks.
- Centralized platforms might be more vulnerable to hacks, data breaches, and insider manipulation because they rely on centralized databases and infrastructure.
Regulatory Compliance
- DeFi operates in a largely unregulated environment, which can offer greater privacy and freedom but may also lead to regulatory uncertainty and compliance risks.
- In CeFi, subject to regulatory oversight and compliance requirements imposed by authorities, offering consumer protection but potentially limiting innovation and privacy.
Here's a comparison chart between DeFi and CeFi:
| Feature | DeFi | CeFi |
| Infrastructure | Built on decentralized blockchain networks (e.g., Ethereum) | Relies on centralized institutions (e.g., banks) |
| Access | Open and permissionless | Always require identity verification and adhere to regulations |
| Transparency | Transparent and auditable on the blockchain | May lack transparency due to proprietary systems |
| Security | Relies on cryptographic security and blockchain consensus mechanisms | May be more vulnerable to hacks and data breaches |
| Regulatory Compliance | Operates in a largely unregulated environment | Subject to regulatory oversight and compliance requirements |
| Innovation | Allows for innovative financial products and services | May be constrained by regulatory compliance and centralization |
Decentralized Finance Components
Smart Contracts
It is a self-executing code stored on a blockchain. They automate agreements and transactions when predefined conditions are met, removing the need for intermediaries.
Blockchain Technology
A simple explanation of Blochhain technology says that it is a distributed ledger system that securely records transactions across a network of computers. It provides transparency, immutability, and trust in a decentralized manner.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Applications built on top of a blockchain that makes smart contracts function. They offer a variety of services without a central authority.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Peer-to-peer marketplaces where users can trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other, eliminating the need for a central exchange. They use smart contracts to trade.
Lending Platforms
Decentralized finance platforms that allow users to lend or borrow cryptocurrencies. Users can earn interest on their holdings by lending them out, while borrowers can access liquidity at competitive rates.
Yield Farming
An investment strategy in DeFi where users lock up their crypto assets in liquidity pools (explained below) to earn rewards or interest. This strategy can be high-risk due to market volatility and impermanent loss (potential loss due to price fluctuations).
Liquidity Pools
Cryptocurrency reserves are locked in smart contracts to make trading on DEXs. Users contribute their assets to these pools and earn fees in return for providing liquidity.
Insurance in DeFi
DeFi insurance does more than just protect your cryptocurrency investments. It gathers premiums from participants into a shared pool, which is then used to help policyholders who experience losses.
DeFi insurance relies on smart contracts, which are self-executing codes on a blockchain. These contracts define policy terms, what events are covered, and how to make a claim. Coverage can include protection against things like smart contract errors, losses from custodians, stablecoin value changes, and even defaults on DeFi loans.
Interoperability and Cross-Chain Protocols
In decentralized finance, interoperability and cross-chain protocols are like bridges connecting isolated islands, enabling a more unified and powerful ecosystem.
Interoperability
Imagine different DeFi protocols existing on separate blockchains, unable to communicate or exchange assets directly. This is where interoperability comes in. It refers to the ability of various blockchain networks to seamlessly interact and exchange data.
Cross-Chain Protocols
These protocols serve as bridges between blockchains, enabling the transfer of cryptocurrency and data across different blockchain ecosystems. This interoperability allows users to access a broader range of DeFi applications and services, irrespective of the underlying blockchain. However, transferring money between blockchains can be extremely expensive.
Benefits of Interoperability and Cross-Chain Protocols
- People can easily move their money between different DeFi platforms on different blockchains. This helps them make more money and use better strategies.
- By letting DeFi work on many blockchains, it allows for new and creative financial ideas to grow.
- Money stuck on one blockchain can now be used in more places, making the whole DeFi system more useful for everyone.
- Using DeFi on any blockchain makes it easier for everyone to use and enjoy.
Examples
Cosmos (ATOM)
Uses a “hub-and-spoke” model, enabling communication between blockchains built on Cosmos SDK.
Polkadot (DOT)
Employs a parachain architecture, allowing independent blockchains to connect to a central relay chain for security and interoperability.
Chainlink (LINK)
Provides decentralized oracle services, bridging the gap between blockchains and real data.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
The regulatory environment surrounding decentralized finance is still a work in progress, characterized by uncertainty and ongoing discussions.
Potential Regulatory Approaches
Regulating Underlying Technologies. Regulators might look at the technology behind blockchain or specific DeFi services that already follow financial rules.
KYC/AML Compliance. Some decentralized finance platforms might have to follow rules like Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) to prevent illegal activities.
Self-Regulation. Decentralized groups that control DeFi platforms might be asked to make their own rules to follow.
Benefits of Clear Regulations
- Clear rules can make DeFi more trustworthy, bringing in bigger investors and users.
- Rules can also protect users by making sure DeFi platforms are transparent and secure.
- Having rules can make DeFi more stable, which might lower how much prices change in the market.
Security Practices for Decentralized Finance Users
In the DeFi, there are risks, but you can protect yourself with these security tips:
Self-Custody
Keep your crypto safe by using a hardware wallet to store your private keys offline, avoiding exchange hacks. Comparing to a software wallet, it is a safer option.
Do Your Research (DYOR)
Before using any DeFi platform, check its reputation, audits, and smart contract code. Stick with established platforms.
Beware of Social Engineering
Be wary of phishing and social engineering scams. Never share your private keys, and double-check website addresses.
Start Small & Gradually Increase Exposure
Begin with a small investment in decentralized finance and gradually increase as you gain confidence and experience.
Keep Software Updated
Make sure your DeFi wallets and browser extensions are up to date to patch any security vulnerabilities.
Disconnect Wallets Regularly
Disconnect your wallet after using a DeFi platform to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Understand Smart Contract Risks
Smart contracts are powerful but can have vulnerabilities. Be aware of potential risks like reentrancy attacks and understand the terms of any DeFi interactions before authorizing transactions.
Benefits of Decentralized Finance
DeFi offers several advantages over traditional financial systems:
Accessibility. DeFi platforms are open to anyone with an internet connection, removing barriers like geographical restrictions or credit checks imposed by traditional banks.
Transparency. Transactions on DeFi protocols are recorded on blockchains, providing a public and immutable record, fostering trust and security.
Control. users retain full control over their funds in decentralized finance. They don't need to rely on third-party custodians like banks, granting them more autonomy.
Potential for Higher Returns. DeFi often offers competitive interest rates on borrowing and lending compared to traditional financial products.
Innovation. DeFi fosters innovation by enabling new financial products and services not readily available in traditional finance.
Efficiency. DeFi transactions can be faster and cheaper compared to traditional systems due to automation enabled by smart contracts.
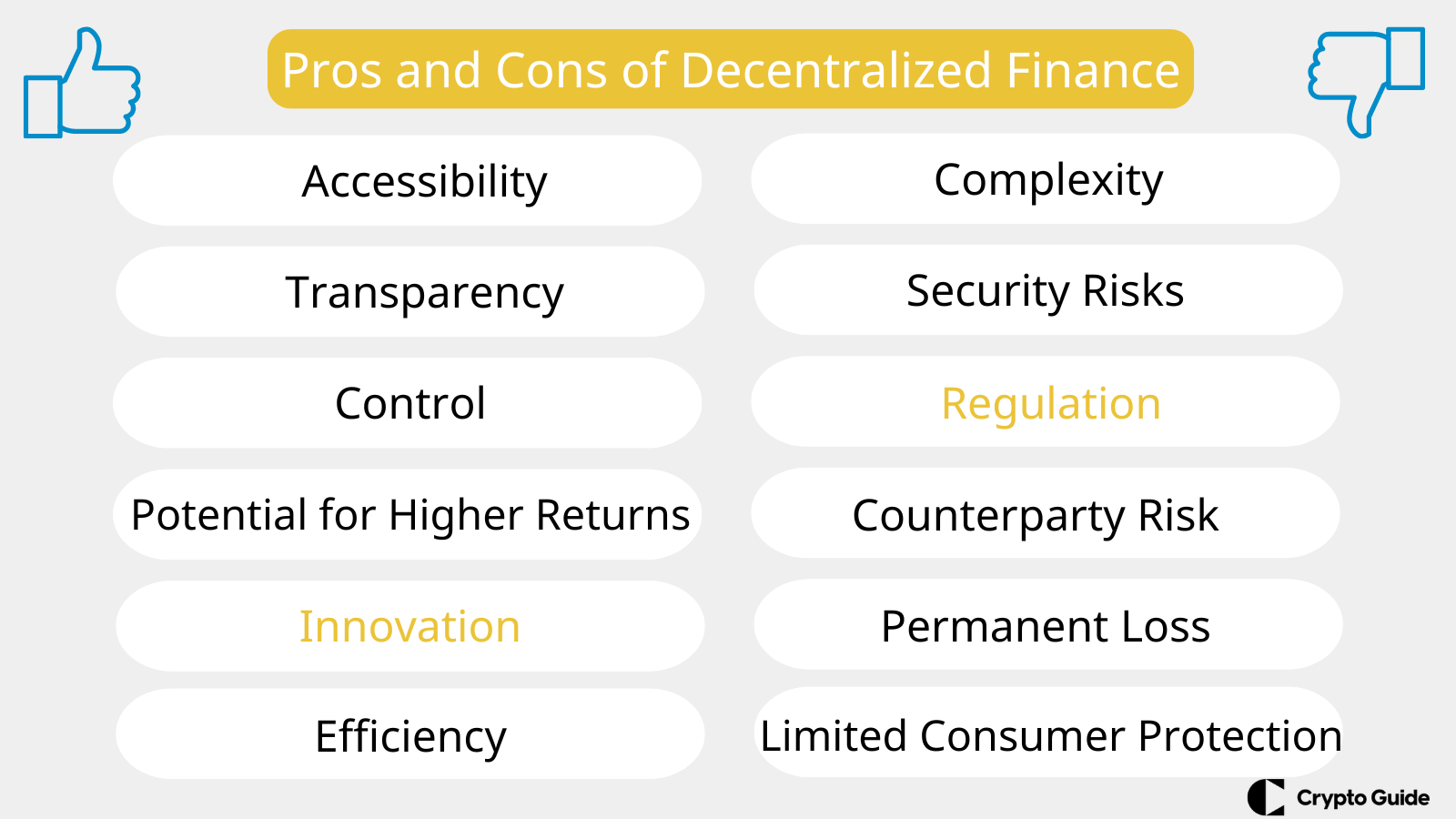
Risks and Downsides
Despite its potential, decentralized finance comes with inherent risks and downsides:
Complexity. DeFi can be complex for beginners. Understanding smart contracts, protocols, and DeFi mechanics requires a significant learning curve.
Security Risks. DeFi platforms are vulnerable to hacks and exploits due to the reliance on smart contracts, which can have bugs or unexpected vulnerabilities.
Regulation. The regulations of DeFi are still under process, which can create uncertainty and potential disruption for the market.
Counterparty Risk. In some DeFi lending scenarios, borrowers may default, leading to losses for lenders. Unlike traditional banks, there's no central entity to guarantee repayment.
Permanent Loss. When you add the assets to DeFi pools, you might face permanent loss if the cryptocurrency prices change a lot.
Limited Consumer Protection. Unlike traditional finance systems with consumer protection mechanisms, DeFi users are responsible for their own security and bear the full risk of their investments.
Real-World Examples
Here are a couple of case studies showcasing real-world applications of decentralized finance:
MakerDAO (DAI Stablecoin)
- The most volatile cryptocurrencies are unsuitable for everyday transactions.
- MakerDAO created DAI, a decentralized stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. Users deposit other cryptocurrencies as collateral to mint DAI, a stable digital asset.
- DAI allows price-stable transactions within DeFi ecosystems, enabling activities like borrowing and lending without worrying about wild price swings.
Aave (Decentralized Lending Platform)
- Limited access to traditional financial services like borrowing and lending, especially in underbanked regions.
- Aave is a peer-to-peer lending platform where users can deposit crypto assets to earn interest or borrow crypto against their holdings.
- Aave empowers individuals to participate in a global lending and borrowing market without relying on banks. It potentially offers better rates and wider access to financial tools.
The Future of DeFi
The future of decentralized finance is promising, with broader adoption likely as blockchain technology becomes more accessible. This could attract more users and increase the value of DeFi protocols.
We may see new DeFi applications beyond lending and trading, such as decentralized insurance and asset fractional ownership. However, increased regulation is expected to address security and consumer protection, potentially stabilizing the space.
Traditional financial institutions might integrate DeFi services, merging DeFi with traditional finance. For this, scalability solutions are needed to address network congestion and high fees.
Security is still a concern, and new measures are needed to build trust. Despite these challenges, DeFi has the potential to impact finances in the future.
FAQ About Decentralized Finance
How do you make money with DeFi?
You can earn interest on your crypto holdings through DeFi lending and staking.
What is an example of a decentralized finance DeFi?
Uniswap, a cryptocurrency exchange platform, is an example of DeFi.
Can I withdraw money from DeFi?
Yes, you can withdraw funds from DeFi protocols to your own wallet.
Is decentralized finance built on blockchain?
Yes, DeFi is built on blockchain technology.
What does DeFi do that banks do not?
DeFi offers peer-to-peer financial services without relying on traditional institutions.
What are the limitations of DeFi?
DeFi can be complex, unregulated, and susceptible to hacks.